Microeconomics MCQs | ECO402 MCQs | Set 10

Microeconomics MCQs | ECO402 MCQs | Set 10
MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)
1) Prospective sunk costs:
a) Are relevant to economic decision-making.
b) Are considered as investment decisions.
c) Rise as output rises.
d) Do not occur when output equals zero.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'd'.
Explanation:
Prospective sunk costs are potential costs associated with future decisions or activities that have not yet been incurred. Sunk costs, by definition, are costs that have been irreversibly incurred and cannot be recovered, regardless of future decisions or outcomes. Since prospective costs refer to potential future costs, they don't occur when output (or activity) is at zero, meaning they haven't been actualized or incurred.
______________________________
2) Which of the following statements demonstrates an understanding of the sunk costs for decision making?importance of
I."Even though I hate my MBA classes, I can't quit because I've spent so much money on tuition."
II. "To break into the market for soap, our firm needs to spend $10 million on creating an image that is unique to our new product. When deciding whether to develop the new soap, we need to take this marketing cost into account."
a) I only.
b) II only.
c) Both I and II.
d) Neither I nor II.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'b'.
Explanation:
______________________________
3) Which of the following statements correctly uses the concept of opportunity decision making?cost in
I."Because my secretary's time has already been paid for, my cost of taking on an additional project is lower than it otherwise would be."
II. "Since NASA is running under budget this year, the cost of another space shuttle launch is lower than it otherwise would be."
a) I only.
b) II only.
c) Both I and II.
d) Neither I nor II.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'a'.
Explanation:
In the first statement, the recognition that the cost of taking on an additional project is lower because the secretary's time has already been paid for reflects an understanding of the opportunity cost. It acknowledges that since the secretary's time is already allocated and paid for, the cost of the additional project is reduced due to the available resource without incurring additional expenses.
______________________________
4) Rabia knows average total cost and average variable cost for a given level of output. Which of the following costs can she not determine given this information?
a) Average fixed cost.
b) Fixed cost.
c) Variable cost.
d) Rabia can determine all of the costs given the information provided.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'd'.
Explanation:
Rabia knows the average total cost, which is the total cost divided by the level of output. She also knows the average variable cost, which is the variable cost divided by the level of output.
Using this information, Rabia can calculate the following:
Total cost: ATC * Output
Variable cost: AVC * Output
Fixed cost: TC - VC
Therefore, Rabia can determine all of the costs given the information provided.
______________________________
5) For any given level of output:
a) Marginal cost must be greater than average cost.
b) Average fixed cost must be greater than average variable cost.
c) Fixed cost must be greater than variable cost.
d) None of the given options is necessarily correct.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'd'.
Explanation:
None of the statements (a, b, or c) is universally true for all levels of output. The relationship between marginal cost and average cost (option a), the comparison of average fixed cost to average variable cost (option b), and the comparison of fixed cost to variable cost (option c) can vary at different output levels and depend on the specific cost structure and the nature of the production function. Therefore, there is no universal relation that always holds among these cost elements for any given level of output.
______________________________
6) Assume that a firm spends $500 on two inputs, labor (plotted on the horizontal axis) and capital (plotted on the vertical axis). If the wage rate is $20 per hour and the rental cost of capital is $25 per hour, the slope of the isocost curve will be:
a) 500
b) 25/500
c) -20/25 or -4/5
d) -25/20 or -5/4
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'c'.
Explanation:
In the case given in the question, the firm has a budget of $500 and the wage rate is $20 per hour and the rental cost of capital is $25 per hour. This means that the firm can hire 25 units of labor or 20 units of capital. The slope of the isocost curve is therefore -20/25 or -4/5.
______________________________
7) The curve in the diagram is called:
a) The income-consumption curve
b) The long-run total cost curve
c) The expansion path
d) The price-consumption curve
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'a'.
Explanation:
The income-consumption curve is often used in microeconomics to demonstrate how an individual or a household's budget constraint changes as their income increases or decreases. It helps to analyze how consumers allocate their income across different goods and services, indicating the quantities they can afford at different income levels while maintaining their preferred consumption patterns.
_______________________
8) A firm employs 100 workers at a wage rate of $10 per hour and 50 units of capital at of $21 per hour. The marginal product of labor is 3 and the marginal product of a rate capital is 5. The firm:
a) Is producing its current output level at the minimum cost.
b) Could reduce the cost of producing its current output level by employing more capital and less labor.
c) Could reduce the cost of producing its current output level by employing more labor less capital.
d) Could increase its output at no extra cost by employing more capital and less labor.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'c'.
Explanation:
The firm can determine the most cost-effective combination of labor and capital by considering the marginal products relative to their costs.
Given the information provided:
Marginal product of labor (MPL) = 3
Marginal product of capital (MPK) = 5
Wage rate (cost of labor) = $10 per hour
Cost of capital = $21 per unit
The firm should compare the marginal product of each input to their respective costs to determine the most efficient use of resources.
The marginal product per dollar spent on each input is calculated by dividing the marginal product by the cost of the input:
For labor: MPL / Wage rate = 3 / 10 = 0.3
For capital: MPK / Cost of capital = 5 / 21 ≈ 0.238
The firm is getting more marginal product per dollar spent on labor compared to capital (0.3 > 0.238). Therefore, it implies that the firm should allocate more resources to labor than capital in its current production scenario to achieve cost efficiency.
So, considering the marginal products and their costs, the firm could reduce the cost of producing its current output level by employing more labor and less capital. Therefore, the correct answer is c) Could reduce the cost of producing its current output level by employing more labor and less capital.
______________________________
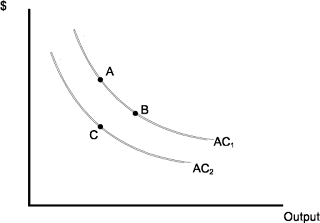
9) A movement from A to C in the above figure may
represent:
a) Economies of scale.
b) Diseconomies of scale.
c) Learning.
d) Economies of scope.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'a'.
Explanation:
The figure shows a downward sloping curve, which means that as output increases, cost per unit decreases. This is the definition of economies of scale.
Diseconomies of scale would be represented by an upward sloping curve, where cost per unit increases as output increases.
______________________________
10) If current output is less than the profit-maximizing output, then the next unit produced:
a) Will decrease profit.
b) Will increase cost more than it increases revenue.
c) Will increase revenue more than it increases cost.
d) Will increase revenue without increasing cost.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer is 'c'.
Explanation:
If the current output is less than the profit-maximizing output, then producing the next unit will move the firm closer to the profit-maximizing level.
The profit-maximizing output level is where marginal cost equals marginal revenue. When current output is below this level, the next unit produced will likely increase revenue more than it increases cost.
______________________________


No comments